
Hints and best practices of SQL Server
As per my understanding we describes the most helpful tips and best practices to write well-optimized SQL queries. It is intended to assist developers as well as database administrators to speed up queries by using hints judiciously and in the best practices. The writing provides practical examples of how hints can be used and how they influence performance, as well as some general guidelines to writing SQL code that performs well.
Imagine SQL Server hints as flags that you fling at the query optimizer:
they direct its thoughts. Hints allow you to clearly push the optimizer to avoid its common preferences and fix a specific execution plan. That will make it faster, but there is no guarantee that applying hints blindly will always be a good idea, you will obtain a less efficient plan in such a case.
What are the indications? SQL server provides you with some of the flavors:
merge hints: These indicate to the optimizer which strategy it should apply to the join, LOOP, MERGE or HASH.
Query hints: These define the grand scheme of things, such as OPTIMIZE FOR or MAXDOP.
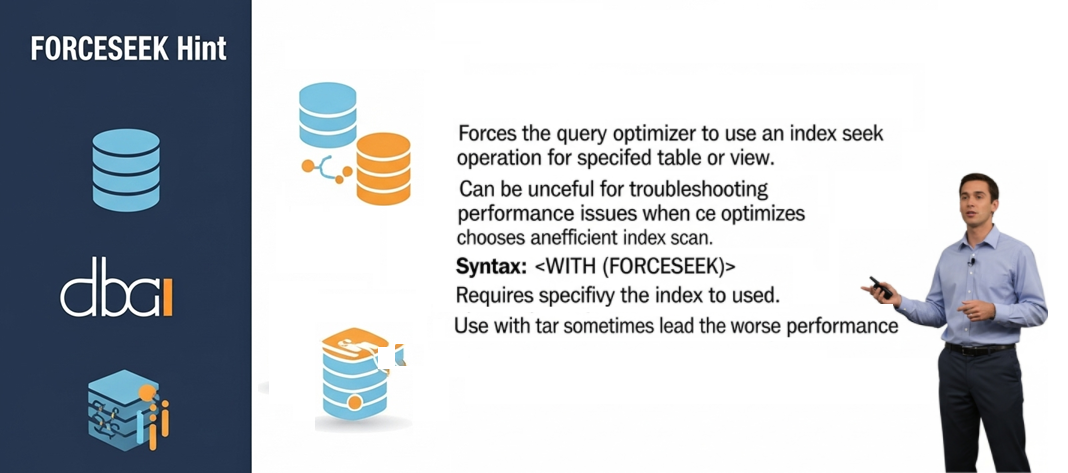
Table hints: Specify particular tables: such as NOLLOCK or INDEX.
hints Examples:
Join Hints
- --Enforce a loop join
- SELECT * FROM Table1 t1
- INNER LOOP JOIN Table2 t2 ON t1.ID=t2.ID;
--Enforce a hash join- SELECT * FROM Table1 t1
- INNER HASH JOIN Table2t2 ON t1.ID=t2.ID;
--Enforce a merge join- SELECT * FROM Table1 t1
- INNER MERGE JOIN Table2 t2 ON t1.ID=t2.ID
Query Hints
- --Optimize for a specific value
- SELECT * FROM Orders
- WHERE CustomerID=123
- OPTION (OPTIMIZE FOR (@CustomerID=123));
- --Limit the degree of parallelism
- SELECT * FROM LargeTable
- OPTION (MAXDOP 4)
Table Hints
- --Use NOLOCK to avoid blocking
- SELECT* FROM Products WITH (NOLOCK)
- WHERE CategoryID=5;
- --Force the use of a specific index
- SELECT * FROM Customers WITH (INDEX (IX_CustomerID))
- WHERE CustomerID=456
A wise use of SQL Server hints is very good as far as performance goes, but it is even better when one follows sound best practices.
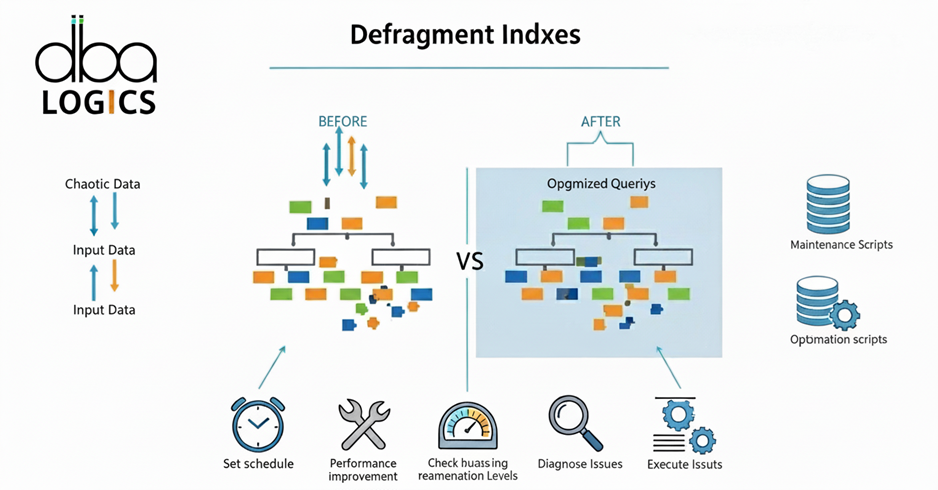
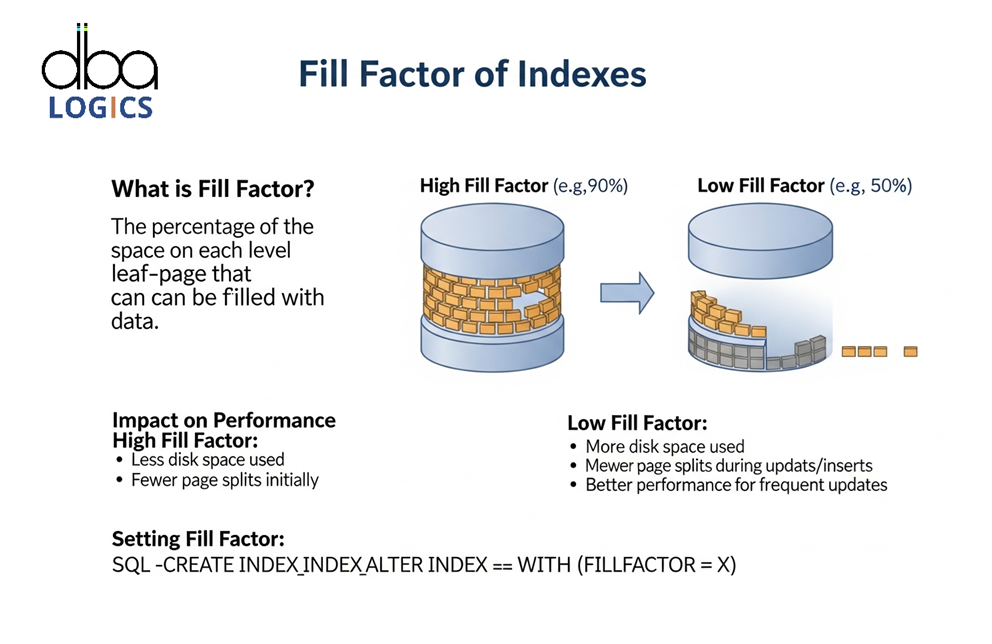
Indexing
Query Design
- Write Queries efficiently: You should always use WHERE in the query so as to narrow the data.
- Do not use SELECT *: Only mention the required column, to minimize I/O.
- Joins: Exercise discretion: Why, When and which type of Join? requirements.
- Simplification of complex queries: Complex queries can break down into easier queries. manageable parts.
- Write Queries efficiently: You should always use WHERE in the query so as to narrow the data.
- Do not use SELECT *: Only mention the required column, to minimize I/O.
- Joins: Exercise discretion: Why, When and which type of Join? requirements.
- Simplification of complex queries: Complex queries can break down into easier queries. manageable parts.
Data Types
- Select Appropriate Data Types: Select a smaller data type big enough to hold the data. the information in order to save space and speed.
- Implicit Conversions to Avoid: Always use like data types in comparisons and in joins escape performance-destroying implicit conversions. Stored Procedures
- Stored Procedures: Stored procedures have the power to enhance performance by running execution plans beforehand and decreasing network traffic.
- Parameterize Queries: Incorporate parameters to stored procedures to ensure that there is no SQL injection and enhance reuse of query plans.
Follow these fundamentals and you will start noticing a significant increase in the speed of queries and a general database performance increase.
- Select Appropriate Data Types: Select a smaller data type big enough to hold the data. the information in order to save space and speed.
- Implicit Conversions to Avoid: Always use like data types in comparisons and in joins escape performance-destroying implicit conversions. Stored Procedures
- Stored Procedures: Stored procedures have the power to enhance performance by running execution plans beforehand and decreasing network traffic.
- Parameterize Queries: Incorporate parameters to stored procedures to ensure that there is no SQL injection and enhance reuse of query plans.
Follow these fundamentals and you will start noticing a significant increase in the speed of queries and a general database performance increase.
Best Practices Examples :
Indexing
- -- Create an index on the CustomerID column
- CREATE INDEX IX_CustomerID ON Customers (CustomerID);-- Rebuild an index
- ALTER INDEX IX_CustomerID ON Customers REBUILD
Query Design
- -- Use a WHERE clause to filter data
- SELECT ProductName, Price
- FROM Products
- WHERE CategoryID = 5 AND Price < 100;
-- Specify only the columns you need- SELECT ProductName, Price
- FROM Products
Data Types
- -- Use the smallest appropriate data type
- CREATE TABLE ExampleTable (
- ID INT,
- Name VARCHAR(50)
- )
Stored Procedures
- --EXEC GetProductsByCategory @CategoryID = 5
- -- Create a stored procedure
- CREATE PROCEDURE GetProductsByCategory (@CategoryID INT)
- AS
- BEGIN
- SELECT ProductName, Price FROM Products
- WHERE CategoryID = @CategoryID;
- END;-- Execute the stored procedure
Conclusion:
Hints and best practices in SQL server are really helpful to fine tune query performance. Although hints can come in handy during certain circumstances, it is important that it is applied with discretion. good knowledge of the query optimizer. Following the best practices, such because good indexing, efficient query design and the use of stored procedures, can will help to greatly optimize a database performance and the efficiency of the system. Regularly it is crucial to monitor and tune up queries in order to gain best performance in the long run.
Hints and best practices in SQL server are really helpful to fine tune query performance. Although hints can come in handy during certain circumstances, it is important that it is applied with discretion. good knowledge of the query optimizer. Following the best practices, such because good indexing, efficient query design and the use of stored procedures, can will help to greatly optimize a database performance and the efficiency of the system. Regularly it is crucial to monitor and tune up queries in order to gain best performance in the long run.






Post Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *