
Explanation of SQL Server Performance Tuning All-In-One Bundle
This is a summary of the SQL Server Performance Tuning All-In-One Bundle is a database performance optimization strategy that covers the entire SQL Server database. It involves several methods and mechanisms used to enhance the performance of queries, databases speed of operation, efficiency and responsiveness of the entire system. With several tuning combined, it is possible to compose music. under specific processes, this bundle aims at getting an optimum performance out of SQL Server environments.
Query Tuning
The optimization of the SQL queries to run faster and use fewer resources is called Query tuning resources. This includes rewritings of queries, the necessary functions, and avoiding the most typical ones. traps that may arise to cause dismal performance.
Techniques:
• Rewriting inefficient queries: Querying queries that inefficiently use set-based operations with constructs, e.g. cursors or scalar functions.
• Appropriate JOINs: The decision of the correct type of JOIN (INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL) depending on the relationships between data and the expected outcomes.
• SELECT * avoidance: Only the required columns to be selected in the SELECT statement minimize the data transmission.
• WHERE clause employment: Sifting information at the earliest point of the query execution plan with suitable conditions of WHERE clause.
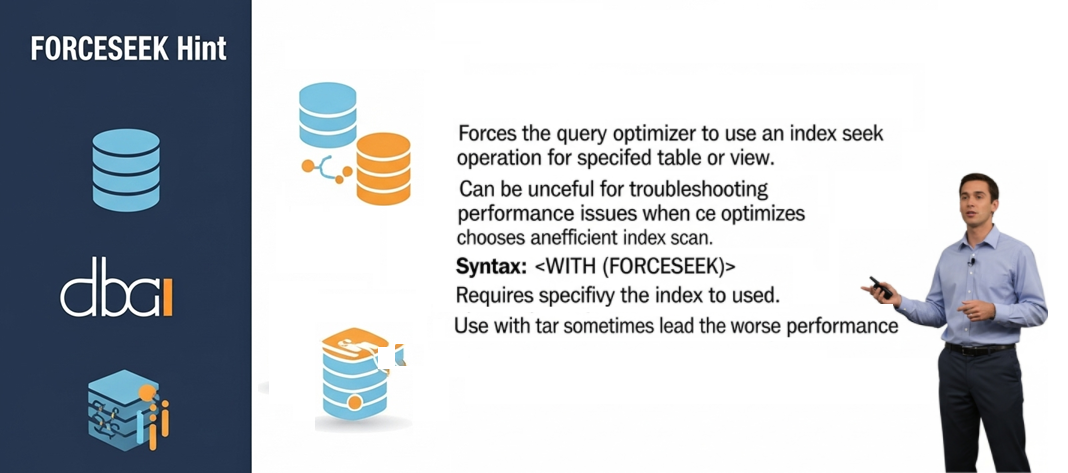
• Query hints: Judicious use of query hints to help the SQL Server optimizer to selecting a given execution plan.
Index Optimization
The indexes play an imperative role in accelerating data retrieval in SQL server. Index optimization deals with designing proper indexes, discarding those which are not necessary or those which can be removed and making sure that indexes are well kept.
Techniques:
• Missing indexes: The Database Engine Tuning Advisor (DTA) or Dynamic Management Views (DMVs) to find out which indexes are missing and potentially creating a more efficient performance for query performance.
• Indexing: Developing of suitable indexes: Developing clustered and non-clustered indexes on Columns that are common in WHERE clause, JOIN conditions and ORDER BY clauses.
• Unused indexes: Removal of indexes not used anymore by any queries in order to minimize storage overhead and increase write performance.
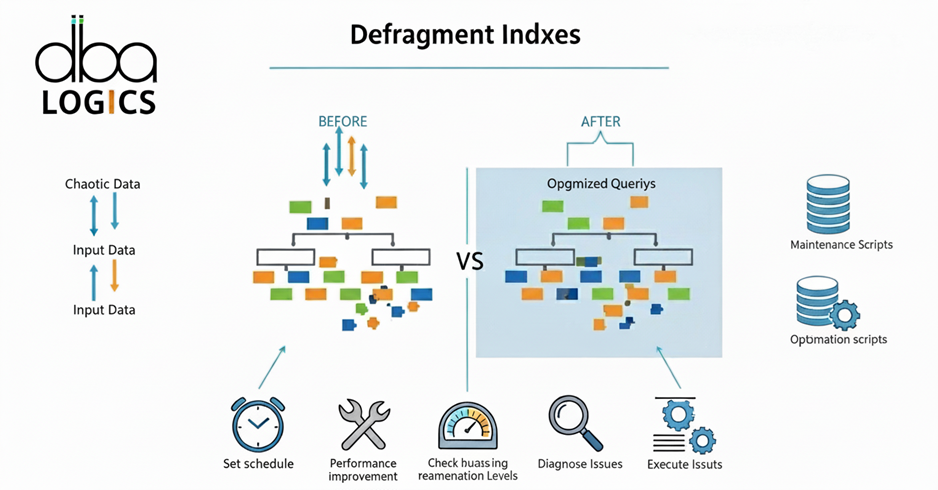
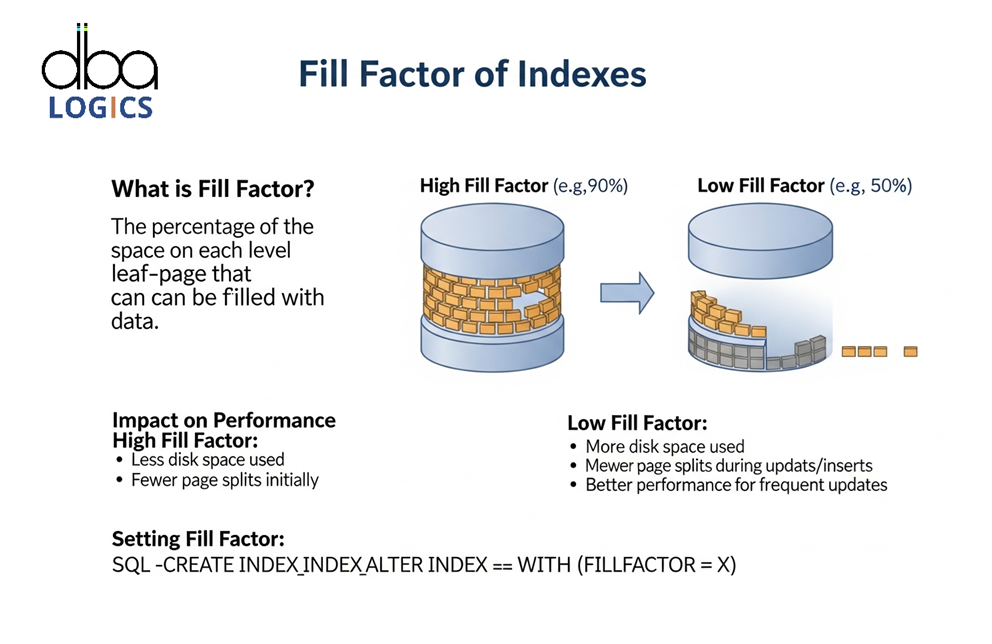
• Rebuilding or Reorganizing indexes: Indexes should be rebuilt or reorganized regularly keep their effectiveness and diminish chunking.
• Filtering indexes: Using indexes to better performance on queries which operate on a selected sub set of data.
Analysis of Execution Plan
The knowledge of the way SQL Server executes queries is a key in determining the performance bottlenecks. Execution plan analysis is a branch of analysis that looks into the plan of execution of the queries. regions in which the optimizer is choosing non-optimally.
Techniques:
• SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS): The graphical representation of the database can be viewed with the use of SSMS Plan of execution of a query.
• Finding costly operators: Finding the operators in the execution plan that use a lot of resources including table scans, sorts and hash joins.
• Interpreting missing index warnings: It is important to look at missing index warnings in the designing an execution plan and developing proper indexes to deal with them.
• Comparing execution plans: Comparing the execution plans of the various versions of a question to determine regressive performances.
• Capturing and Analyzing Extended Events: Analysis and capture of Extended Events to get a deeper insight query execution insight.
Maintenance and Statistics
Statistics give the SQL Server 2008 optimizer the details concerning how the data is distributed indexes and tables. It is of great importance to keep the statistics updated and maintain the indexes that the optimizer makes intelligent decisions.
Techniques:
• Periodic update of statistics: Setting SQL Server to automatically update statistics on a regular basis.
• FULLSCAN or SAMPLE: Selecting the right sampling method to use in updating statistics founded on the volatility of data and the size of data.
• Indexes: Rebuild / reorganize indexes as frequently as possible to minimize fragmentation and enhance performance.
• With Ola Hallengren maintenance scripts: The Ola Hallengren maintenance scripts are implemented maintenance scripts to maintain the database thoroughly.
TempDB Optimization
TempDB is a SQL system database that is utilized by SQL server as a temporary storage mechanism. Configuring Better performance TempDB can enhance the performances of the whole system.
Techniques:
• Assigning several data files: Multiple-data files to TempDB in order to minimize contention.
• Appropriately sizing TempDB: To be sure that TempDB is sized well meet the work load.
• Separation of TempDB: Separation of TempDB, i.e. putting it on fast storage, such as SSDs, to improve performance.
• TempDB usage: monitoring the usage of TempDB to determine possible bottlenecks.
• Trace flags: Coming up with a better performance of Temp DB by use of trace flags (such as 1118).
Memory &CPU Monitoring
A system-level bottleneck identification is imperative to the optimization of the SQL Server performance. Memory and CPU tracking is a process of monitoring the usage of the resources in an attempt to locate the spots of improvement.
Techniques:
• With Performance Monitor: monitoring CPU usage with the Performance Monitor, disk I/O, memory usage and networks.
• DMVs: Monitoring the use of SQL Server and the consumption of the CPU using DMVs And I/O statistics.
• Detecting memory pressure: Detection of memory pressure and its remedy by the increment of memory, or optimization of queries.
Identifying CPU bottlenecks: Identification of CPU bottlenecks and calibration of the same To optimize queries or to modify the hardware.
Avoiding Blocking/Deadlocks
Blocking and deadlocks may also have severe performance consequences on SQL Server. Avoiding these, The problem of issues is the application of suitable levels of isolation and indexing.
Techniques:
• Appropriate isolation levels: With respect to the appropriate level of isolation, the following levels can be selected the requirements of the application.
• Proper indexing: Making indexes appropriately to minimize chances of blocking and deadlocks.
• Transactions kept short: Keeping transactions short is done to reduce the length of locks.
• READ COMMITTED SNAPSHOT isolation level: With regards to the READ Made SNAPSHOT isolation level committed in order to decrease blocking.
• Blocking and deadlocks monitoring: The observation of blocking and deadlocks and responding to them in a timely way.
Conclusion:
The SQL Server Performance Tuning All-In-One Bundle is a broad approach that covers query tuning, indexing, execution plans analysis and tuning of the system. The combined use of these techniques can keep the database fast, stable and efficient environment. Long-term performance has to do with regular monitoring and tuning. By with proactive approach to solving performance problems, organizations are in a position to guarantee their SQL Server databases are still answering their applications and users.






Post Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *