Performance
Becoming a Successful Database Administrator (DBA)
A Database Administrator (DBA) is the one who designs, implements, maintains, and solves database problems. The major objective of a DBA is making the...
LEN() vs DATALENGTH() in SQL Server – Easy and Clear!
LEN() function in SQL Server provides the count of the total characters in a string not counting rear spaces; DATALENGTH() gives out the total numbers...
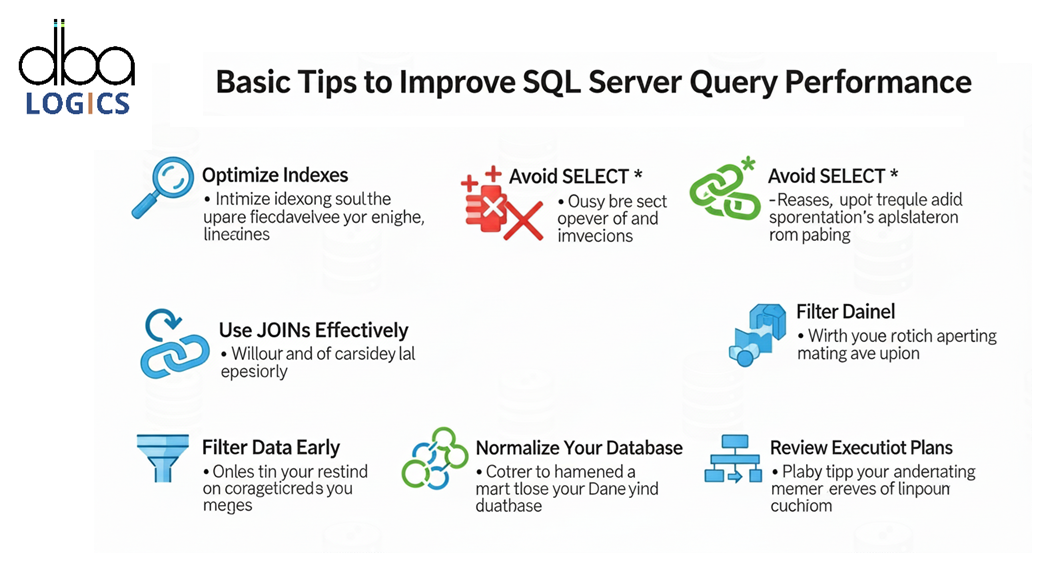
Basic Tips to Improve SQL Server Query Performance
The SQL Server has optimal query execution, proper indexing and frequent modification of the system based on the data load very efficiently.
Finding Top 10 Queries That Use CPU in MS SQL Server
This query can be used to get the 10 most CPU consuming SQL statements and will assist the DBA with the identification and optimization of costly bott...
SQL Server CASE Statement – Simple Explanation
The CASE statement in SQL Server is used to add conditional logic to your queries. It works like an IF-THEN-ELSE statement, allowing you to return dif...
Explanation of SET STATISTICS PROFILE in SQL Server
In SQL Server, SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON gives the actual execution plan that provides the details about the queries that are run on the database as w...
Understanding Relative Query Cost in SQL Server
Relative Query Cost in SQL Server refers to the estimated percentage of resources (like CPU and I/O) used by each part of a query or by multiple queri...
Explanation of Unused Indexes in SQL Server
Unused Indexes are indexes that exist in a table but are rarely or never used by SQL Server for reading data. These indexes consume storage and slow d...
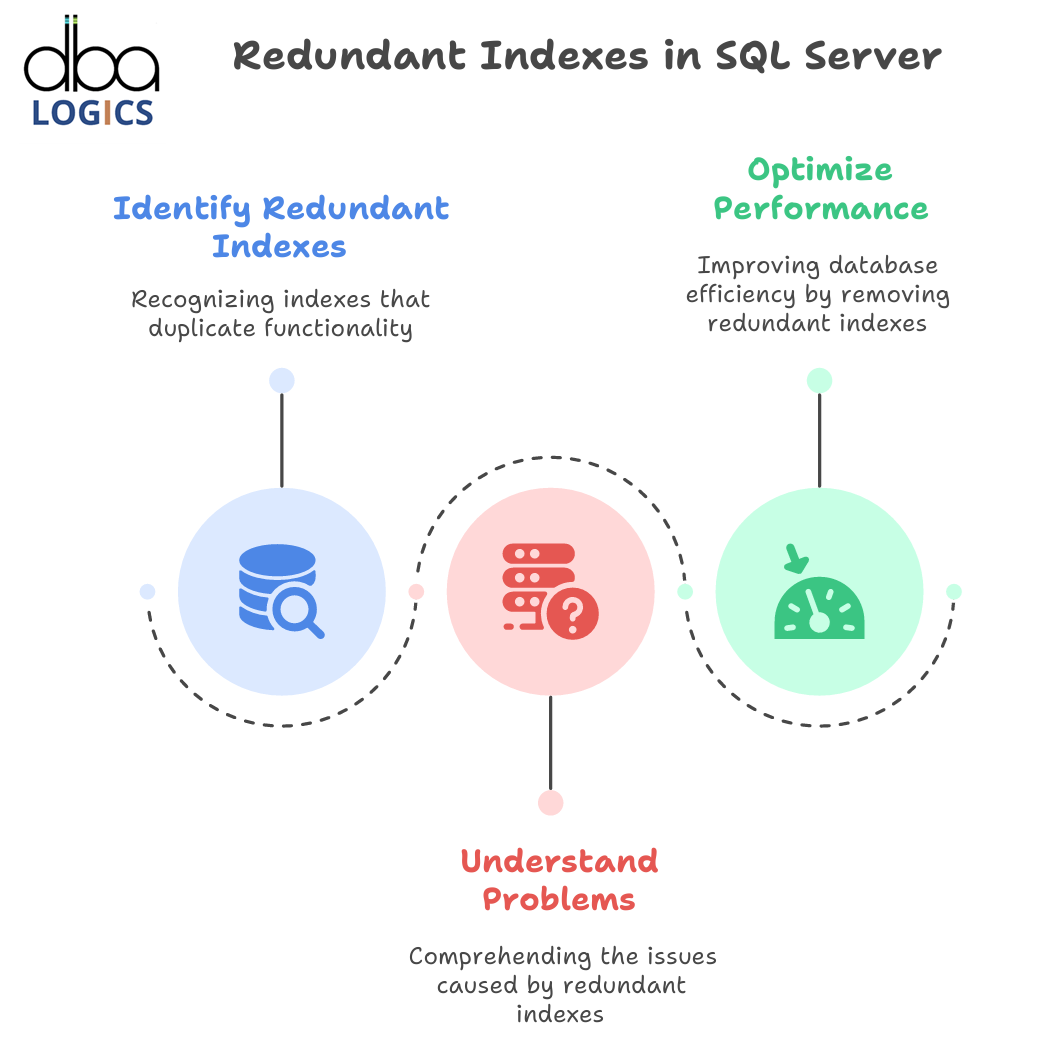
Learning SQL about Redundant Indexes Server
Redundant indexes in SQL Server are duplicating or overlapping indexes which both consume unnecessary space and can negatively affect performance to t...
Explanation of Removing Table Spool Operator in SQL Server
A Table Spool makes part of query result to be packed pool together in tempdb, which aids SQL Server in data reuse by reusing the similar variable res...
Explanation of SQL Server Performance Tuning All-In-One Bundle
The All-In-One SQL Server Performance Tuning Bundle provides professional tools, scripts and guidelines in order to minimize query execution time, use...
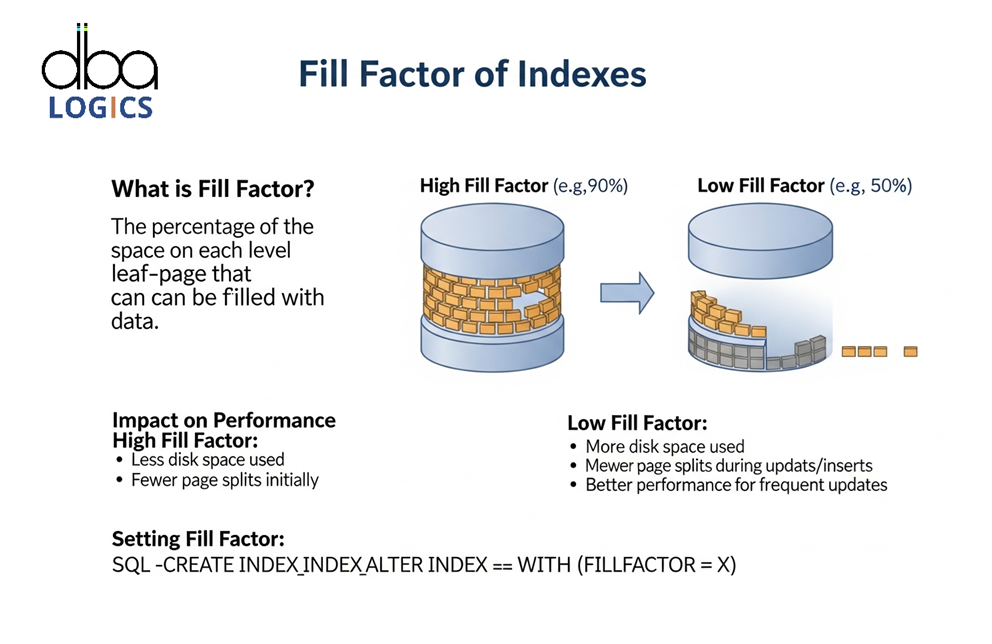
Explanation of Find Fill Factor of All Indexes in a Database in SQL Server
Fill Factor is one of the options that deal with the amount of space to leave in every index page
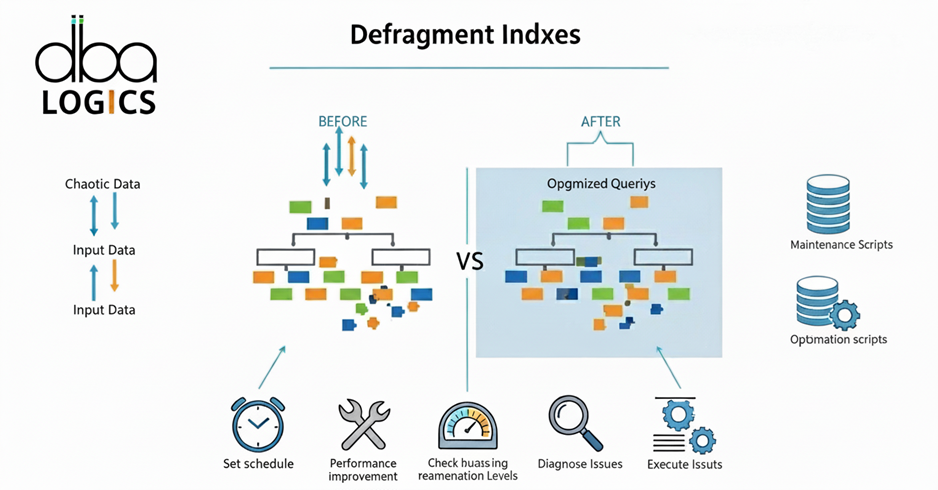
Explanation to Defragment All Indexes in a Database
Rebuilding all indexes enhances database by re-ordering or re-assembling fragments in all indexes within all the tables of the database.
Explanation of Fragmented Indexes in a Database in SQL Server
Identify fragmented indexes in SQL Server to improve query performance and optimize storage by rebuilding or reorganizing inefficient index structures...
Explanation of Find Tables Without Clustered Index in SQL Server
Checks SQL Server tables which do not have clustered indexes, but assist in improving performance, by revealing tables which can also be indexed.
SQL Server Statistics Updates: A Deep Dive
Updates The statistics that are used by the query optimizer to select efficient execution plans are maintained through the SQL Server statistics updat...
Hints and best practices of SQL Server
When you are running SQL Server, there are a couple of well-worn maneuvers that keep things moving. Table index, query tune and monitor the logs so th...
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS: A Deep Dive with Practical Examples
DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS examines indexes and data rows of a table and displays the finding.
Understanding COUNT(*), COUNT(1), and COUNT(column) in SQL Server
COUNT(*) counts the total rows, COUNT(1) counts as COUNT(*), and COUNT(column) counts only non- NULL values of column.
SQL Server 2025 Release : A Detailed Overview
SQL Server 2025 is expected to have more advanced performance, AI integration, security, cloud-native capabilities, and scalability in modern enterpri...
Understanding Isolation in the Database Transactions
The isolation of database transactions makes the operations independent of each other which prevents a conflict, ensures the consistency of data and e...
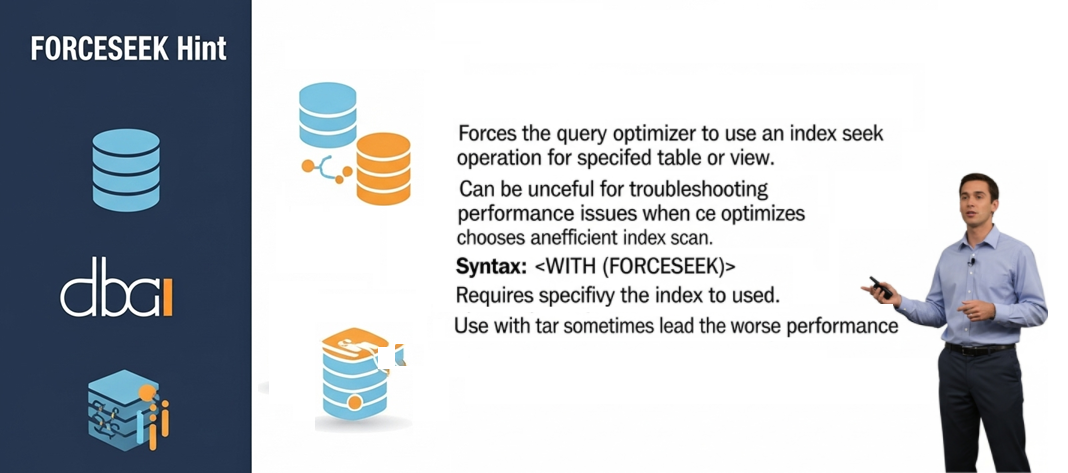
FORCESEEK Hint in SQL Server: A Deep Dive
SQL Server FORCESEEK hint for sql server is used to make the optimizer search through the index, which enhances the performance of the query by elimin...