T-SQL Queries
SQL Command Types Explained: DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL
Study the role and the distinction between the types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, and DCL, and TCL utilized to control and create the structure of the d...
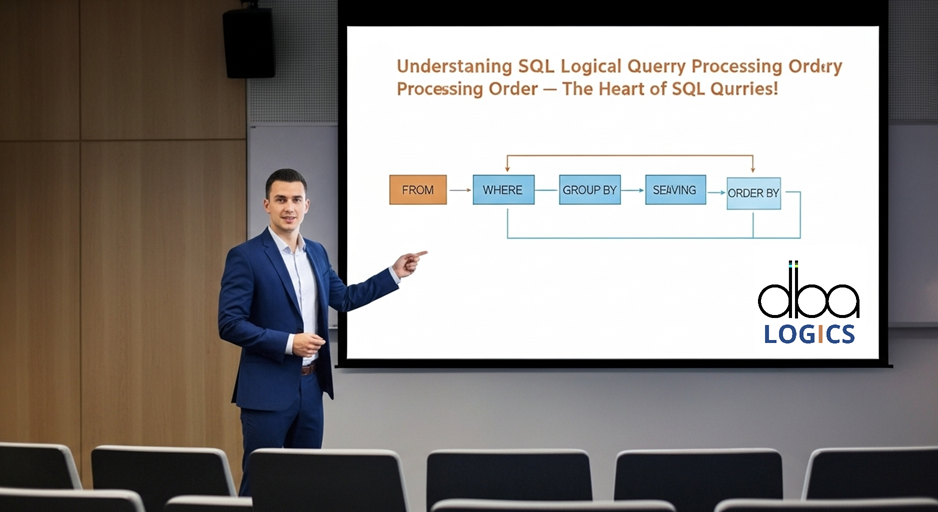
Understanding SQL Logical Query Processing Order – The Heart of SQL Queries!
SQL processes queries in a specific logical order, not writing order. Understanding this flow helps build accurate and optimized queries.
SQL Server Joins Explained Simply
In SQL Server, joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them.
LEN() vs DATALENGTH() in SQL Server – Easy and Clear!
LEN() function in SQL Server provides the count of the total characters in a string not counting rear spaces; DATALENGTH() gives out the total numbers...
SQL Server CASE Statement – Simple Explanation
The CASE statement in SQL Server is used to add conditional logic to your queries. It works like an IF-THEN-ELSE statement, allowing you to return dif...
Mastering ISNULL() Function in SQL Server
The ISNULL() function in SQL Server is used to replace NULL values with a specified replacement value.
ISNULL vs COALESCE: Key Differences in SQL Server
ISNULL() and COALESCE() functions in SQL Server are commonly used to replace or manage NULL values in query results.
Mastering CHARINDEX in SQL server
CHARINDEX in SQL Server returns the starting position of a substring within a string. It helps in locating text patterns and supports optional start p...
Masting Common Table Expressions in SQL Server
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) in SQL Server provide a temporary result set for organizing complex queries and improving code readability.
Mastering SQL Server Ranking Functions: RANK, DENSE_RANK, ROW_NUMBER, and NTILE
RANK functions assign ordered numbers to rows: RANK, DENSE_RANK, ROW_NUMBER, and NTILE help with sorting and grouping.
Understanding the RANK() Function in SQL with Practical Examples
The RANK() function is used to number the rows in partitions, with ties for ties, to sort and rank the results of a query.
Mastering in DENSE_RANK() Function in SQL with Practical Examples
DENSE_RANK() produces unique ranked numbers without gaps in them in the event of ties.
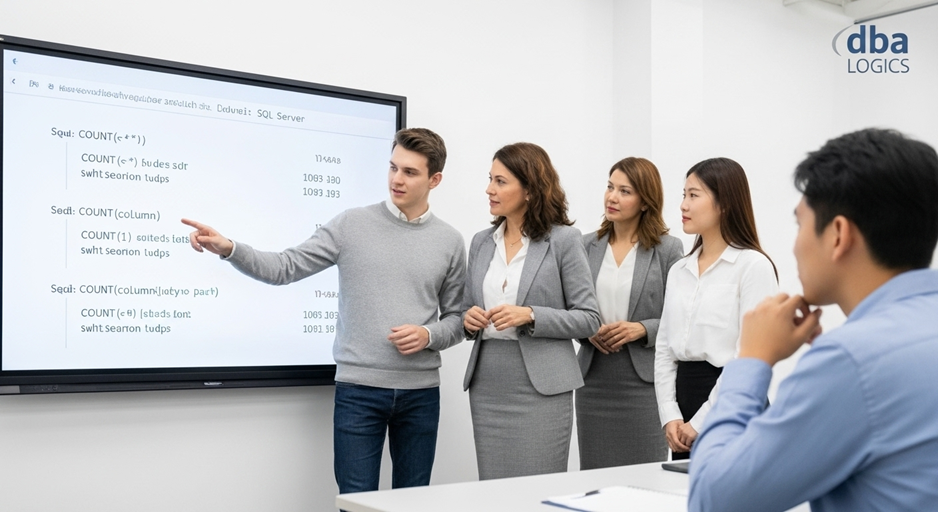
Understanding COUNT(*), COUNT(1), and COUNT(column) in SQL Server
COUNT(*) counts the total rows, COUNT(1) counts as COUNT(*), and COUNT(column) counts only non- NULL values of column.
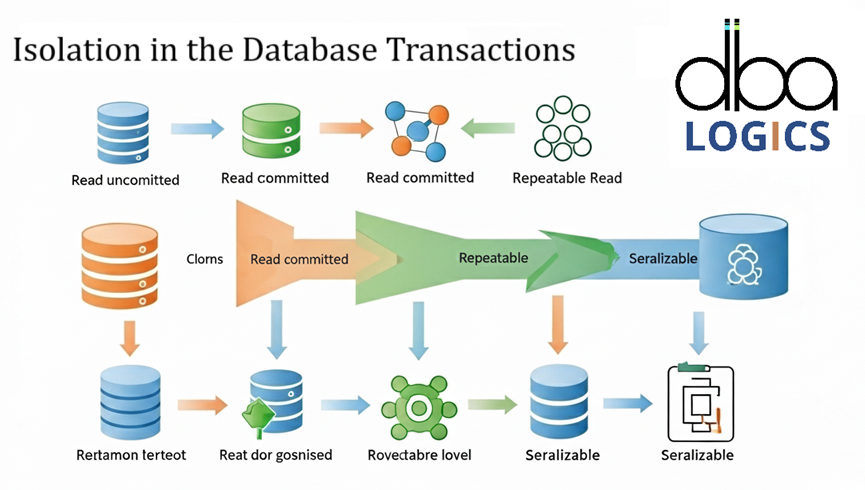
Understanding Isolation in the Database Transactions
The isolation of database transactions makes the operations independent of each other which prevents a conflict, ensures the consistency of data and e...