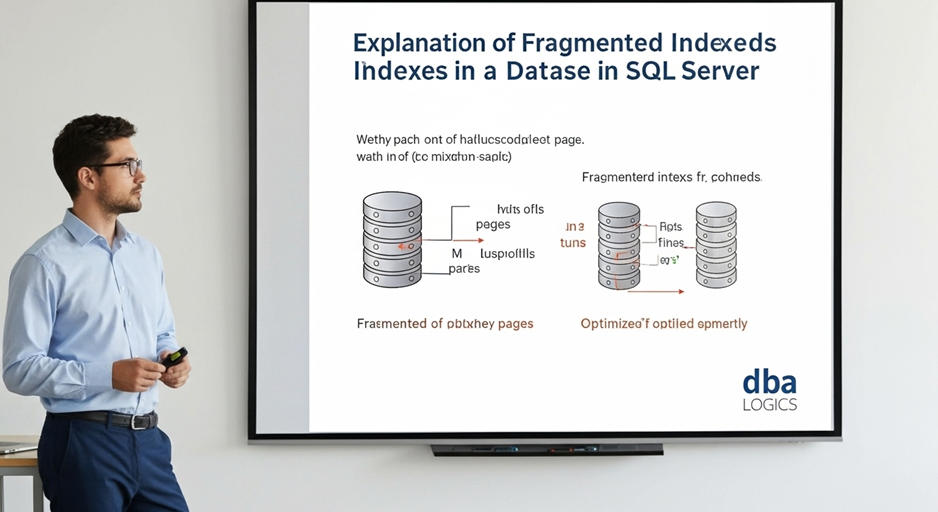
Explanation of Fragmented Indexes in a Database in SQL Server
This report offers a SQL script that can be used to discover fragmented indexes in a SQL Server database. Index fragmentation has the potential to strongly affect query performance and this script will aid database administrators in evaluating index health, and deciding what types of maintenance to execute on indexes, namely reorganization or index rebuilding.
Script to Identify Fragmented Indexes
The next script reads details of fragmented indexes of a SQL Server database along with the schema name, table name, index name and fragmentation percentage, and the number of pages.
Example Script:
- SELECT
- OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(ips.object_id) AS SchemaName,
- OBJECT_NAME(ips.object_id) AS TableName,
- i.name AS IndexName,
- ips.index_id,
- ROUND(ips.avg_fragmentation_in_percent, 2) AS FragmentationPercent,
- ips.page_count
- FROM
- sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, 'LIMITED') AS ips
- JOIN
- sys.indexes AS i ON ips.object_id = i.object_id AND ips.index_id = i.index_id
- WHERE
- i.index_id > 0 -- exclude heaps
- AND ips.page_count > 100 -- ignore small indexes
- ORDER BY
- FragmentationPercent DESC;
The given script returns the result set as shown in the following columns:
- SchemaName: Scheme of the table.
- TableName: Table name.
- IndexName: Self-explanatory.
- index_id: an ID of the index.
- FragmentationPercent: The fragmentation in the index as percentage.
- Page_Count: The number of pages that are used by the index.
- SchemaName: Scheme of the table.
- TableName: Table name.
- IndexName: Self-explanatory.
- index_id: an ID of the index.
- FragmentationPercent: The fragmentation in the index as percentage.
- Page_Count: The number of pages that are used by the index.
Depending upon the Fragmentation percentage, you will be able to decide what to do:
- 0-5% Fragmentation: Fair normal level; nothing to be done.
- 5-30 % Fragmentation: You may want to reorganize the index. Reorganizing is weightless reordering of the leaf nodes of the index that is performed online and with limited disruption.
- More than 30Percent Fragmentation: Rebuild the index. Rebuilding develops something new copy of the index which is more effectual on highly fragmented indexes. This will usually consume more resources and most probably move into downtime as compared to operation the version of SQL server and the options employed.
- 0-5% Fragmentation: Fair normal level; nothing to be done.
- 5-30 % Fragmentation: You may want to reorganize the index. Reorganizing is weightless reordering of the leaf nodes of the index that is performed online and with limited disruption.
- More than 30Percent Fragmentation: Rebuild the index. Rebuilding develops something new copy of the index which is more effectual on highly fragmented indexes. This will usually consume more resources and most probably move into downtime as compared to operation the version of SQL server and the options employed.
Rebuilding Vs. Reorganizing Indexes
Reorganizing: - Takes advantage of the available index pages.
- Resorts pages at leaf level in the logical order.
- More cost effective.
- In majority of cases it can be done online.
- Better when level of fragmentation is small.
Rebuilding: - Makes a new copy of index.
- Needs additional resources (disk space and CPU).
- Online performance is possible in Enterprise Edition.
- more practical with increased degrees of fragmentation.
- Keeps statistics afloat as part of the process.
Reorganizing:
- Takes advantage of the available index pages.
- Resorts pages at leaf level in the logical order.
- More cost effective.
- In majority of cases it can be done online.
- Better when level of fragmentation is small.
Rebuilding:
- Makes a new copy of index.
- Needs additional resources (disk space and CPU).
- Online performance is possible in Enterprise Edition.
- more practical with increased degrees of fragmentation.
- Keeps statistics afloat as part of the process.
Conclusion:
This script lists all fragmented indexes in your database with their fragmentation level. Use it to monitor index health and decide which indexes to reorganize (if 5–30% fragmented) or rebuild (if over 30%). Regular monitoring improves database performance and keeps queries running efficiently.
This script lists all fragmented indexes in your database with their fragmentation level. Use it to monitor index health and decide which indexes to reorganize (if 5–30% fragmented) or rebuild (if over 30%). Regular monitoring improves database performance and keeps queries running efficiently.







Post Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *